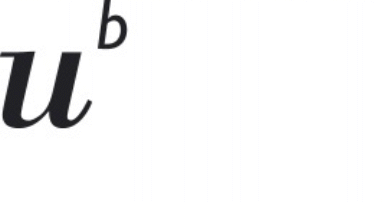|
Trypanosoma brucei as a pathogen
T. brucei belongs to the Trypanosomatidae,a large family of flagellated parasitic protozoa that are responsible for diseases in humans and animals. Members of this family cause human sleeping sickness and nagana of cattle in Africa (Trypanosoma brucei spp.), Chagas disease in Latin America (Trypanosoma cruzi) and different forms of leishmaniasis (Leishmania spp.) in much of the tropical and subtropical world.
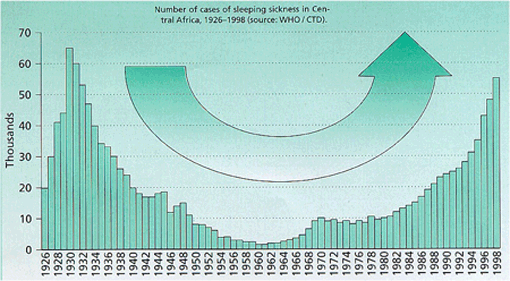
Human sleeping sickness - whose incidence is increasing again since the sixties - is invariable fatal if untreated (WHO). No vaccines exist and many drugs have been in use for over forty years. New more efficient drugs are desperately needed since treatment of late stage human sleeping sickness with melarsoprol - still the only drug available to treat this stage of the disease – is complex and causes serious side effects of which almost a thousand people die each year. Moreover, in some regions of Africa resistance against melarsoprol is emerging.
Incidence of sleeping sickness (from Karger Gazette 63, 1999)
|
 |